Lando is a Docker based development tool, which is much faster than Vagrant-based tools, since processes are run in containers directly on the host machine.
The requirements on the host machine. Note that a database is not required:
- Docker
- Lando
- PHP
- Composer
Install Docker
Follow the instructions on these pages;
https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/docker-ce/ubuntu/#install-using-the-repository
https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/linux-postinstall/
Fix missing ~/.docker/config.json file, from https://www.reddit.com/r/docker/comments/74cok4/missing_configjson/
# "$HOME/.docker/config.json -- If there is no such file (and/or folder) you can create it. For example"
# create folder
mkdir $HOME/.docker
# create config with empty object
echo "{}" > $HOME/.docker/config.json
Manage Docker as a non-root user
# https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/linux-postinstall/#manage-docker-as-a-non-root-user
sudo chown "$USER":"$USER" /home/"$USER"/.docker -R sudo chmod g+rwx "$HOME/.docker" -R
Install PHP
PHP packages for running Drupal 9 in Ubuntu 20.04, as well as installing Composer:
sudo apt install php-cli php-curl php-gd php-mbstring php-sqlite3 php-xml php-zip
Note: Installing php-cli and not php prevents Apache from being installed. Also, php-sqlite3 is required if you want to test Drupal via the Drupal Quick Start Command.
By not defining the PHP version, the latest available version will be installed automatically:
$ dpkg --get-selections | grep -i php php-cli install php-common install php-curl install php-gd install php-mbstring install php-sqlite3 install php-xml install php7.4-cli install php7.4-common install php7.4-curl install php7.4-gd install php7.4-json install php7.4-mbstring install php7.4-opcache install php7.4-readline install php7.4-sqlite3 install php7.4-xml install
Ubuntu 18.04 comes with PHP 7.3 by default, and this is the error, when running composer create-project with too low PHP-version:
Your requirements could not be resolved to an installable set of packages.
Problem 1
- drupal/core 9.0.2 requires php >=7.3 -> your PHP version (7.2.32) does not satisfy that requirement.
...
In theory, you can prevent Composer from finding issues with un-resolvable PHP version requirements by defining PHP version in a .composer/config.json file, but it doesn't seem to work. An easier fix is upgrading the host PHP version to as close as the version your Lando projects will be running.
Upgrade to a newer PHP version, note the different Lando and host version:
$ lando php -v PHP 7.3.19 $ php -v PHP 7.3.20-1
Install Composer
From https://getcomposer.org/download/
# check if /home/your_username/.local/bin is part of the registered PATH:
echo $PATH
# if not, add this line to ~/.bashrc
export PATH="/home/your_username/.local/bin/:$PATH"
# make it take effect
source ~/.bashrc
Download the latest stable composer.phar manually, see also https://getcomposer.org/download/
wget https://getcomposer.org/composer-stable.phar # finish installation, and commands to check and update mkdir ~/.local/bin/ # create folder if it doesn't exist mv composer-stable.phar ~/.local/bin/composer chmod a+rx ~/.local/bin/composer # make executable whereis composer composer composer selfupdate # switch to Composer 1 from Composer 2 composer self-update --1
Install Lando
Follow the instructions on these pages;
https://github.com/lando/lando
https://docs.lando.dev/basics/installation.html#debian
# download Latest release wget https://files.devwithlando.io/lando-stable.deb # verify version dpkg --info lando-stable.deb # install Lando sudo dpkg --install lando-stable.deb # remove install file (space prevents saving it in command line history) rm lando-stable.deb
Add Lando certificates in Firefox
NOTE: You have to start Lando to generate the certificates first.
To avoid a "Secure Connection Failed" or "Did Not Connect: Potential Security Issue" and "Error code: SEC_ERROR_BAD_SIGNATURE" in Firefox, remember to add the certificates:
https://docs.lando.dev/config/security.html#debian
Take special care to import the Lando CA certificate afterwards: https://docs.lando.dev/config/security.html#ubuntu-with-firefox
Switch between Lando versions, or install a new version
To switch between Lando versions, or install a newer version, first clean up and delete old Docker containers (see "Extra Docker tips" below), then uninstall and remove the old version:
# uninstall Lando and delete config folder, the extra space before the "rm" command excludes the command from being added to your terminal history sudo dpkg -P lando rm ~/.lando -rf
Next, install a specific version of Lando:
wget https://github.com/lando/lando/releases/download/v3.0.0-rc.22/lando-v3.0.0-rc.22.deb sudo dpkg -i lando-v3.0.0-rc.22.deb rm lando-v3.0.0-rc.22.deb
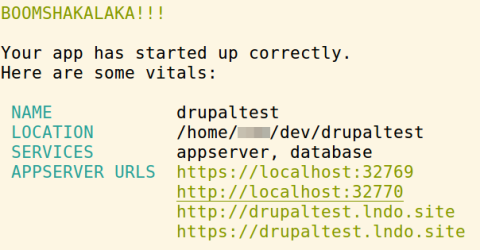
Drupal 8 in Lando Docker
# create and enter your dev-directory, for example in ~/dev folder # NOTE: don't call it .lando! This is where Lando configuration is written mkdir ~/dev cd ~/dev # create a Drupal project. Assumes that you have Composer installed. composer create-project drupal/recommended-project drupaltest # cd into the created directory. cd drupaltest # launch the interactive session. lando init # or just specify the Drupal 8 recipe. lando init --recipe drupal8 --webroot web --name drupaltest # show info lando info # start lando lando start # install Drupal with Drush lando drush site-install --db-url=mysql://drupal8:drupal8@database/drupal8 --account-pass=content -y # log into your new site lando drush uli -l http://drupaltest.lndo.site # download Admin Toolbar module composer require drupal/admin_toolbar # enable Admin Toolbar module lando drush en admin_toolbar admin_toolbar_tools -y # clear cache lando drush cache-rebuild # destroy the Lando app and delete the folder lando destroy cd .. chmod -R 775 drupaltest && rm drupaltest -rf; # add these aliases to your ~/.bashrc file to shorten "lando drush" commands # activate with closing the terminal, source ~/.bashrc is not enough alias drush='lando drush'
Sources
https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/docker-ce/ubuntu/
https://colorfield.be/blog/drupal-and-docker-the-easy-way-with-lando
Define Drush columns
By default, Lando sets this at 256 columns, for better readability you can tweak this. Set globally in ~/.lando/config.yml:
appEnv: COLUMNS: '120'
Insert with this:
printf "appEnv:\n COLUMNS: '120'" >> ~/.lando/config.yml
Set per project, in .lando.yml:
services:
appserver:
overrides:
environment:
COLUMNS: '120'
Check if it looks good by typing drush, or with this:
$ lando ssh -s appserver -c env | grep -i col COLUMNS=120
Working offline with Lando
By default, you can't start Lando without internet access, since it uses an online service to look up a DNS entry: "Lando accomplishes this with an actual ON THE INTERNET wildcard DNS entry that points all lndo.site subdomains to localhost/127.0.0.1. This means that if you lose your internet connection, you will not be able to visit your app at these addresses."
The solution is Working Offline or Using Custom Domains by adding your custom domain in your /etc/hosts file, like this:
# Get my `lndo.site` domain to work offline 127.0.0.1 myapp.lndo.site # If you have defined an extra domain 127.0.0.1 admin.myapp.lndo.site
IMPORTANT: You will need to do a lando poweroff to apply these changes.
Extra Docker tips
Status and clean up and delete containers, for more info, see https://colorfield.be/blog/cleaning-lando-containers
# display all containers
docker ps --all --format "table {{.ID}}\t{{.Image}}\t{{.Command}}\t{{.CreatedAt}}\t{{.Status}}\t{{.Names}}"
# stop, remove and remove images
docker kill $(docker ps -q)
docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)
docker rmi $(docker images -q)
# to nuke everything
docker system prune -a
# disable Docker from starting on boot
# check Docker status
sudo systemctl list-unit-files | grep -i docker
# result
docker.service enabled
docker.socket enabled
# disable Docker from starting on boot
sudo systemctl disable docker.service
sudo systemctl disable docker.socket
Fix VPN Docker IP conflict
Dockers default IP ranges at 172.17.* 172.18.* 172.19.* might conflict with your VPN, if it uses the same ranges.
Adding this to `/etc/docker/daemon.json` and restarting Docker updates both `docker0` and the bridges (like `br-eb18f822dc96`):
{
"default-address-pools":
[
{"base":"172.90.0.0/16","size":24}
]
}
Remove unused Docker networks, if they conflict with VPN connection
docker network prune
Result
$ ip addr | grep 172
inet 172.90.0.1/24 brd 172.90.0.255 scope global docker0
inet 172.90.1.1/24 brd 172.90.1.255 scope global br-c71a376aa530
inet 172.90.2.1/24 brd 172.90.2.255 scope global br-9a2279ba5e4f
inet 172.90.3.1/24 brd 172.90.3.255 scope global br-ff55447fdd53
Some suggest this in `daemon.json`, but it only updates the IP for `docker0`, but not the bridges:
{
"bip" : "172.90.0.1/24"
}
stop and start Docker again
sudo systemctl stop docker sudo systemctl start docker